
You have reached that time in life where you feel ready to settle down and live the homeowner’s life. So you want a house. And you want to decorate it. You keep seeing those Wayfair commercials and thinking, “Hey, I have just the place for that.” Then, you realize you do not. Actually, you live in a tiny apartment. Or a mobile home. Or an RV. Maybe, you still live with your mom and dad. Bummer. Uh oh.
How to Find a No Income Verification Mortgage Loan
You just got a notion to search for mortgage requirements. You found out how hard it can be to qualify. What is that income check thing?
When you apply for a standard mortgage, you learn that the lending institution will not only check your credit, it will check your income. You must have verifiable income at an appropriate level for them to approve you.
That means you must provide your pay stubs, your employer’s name, phone number and address, your W-2s, your tax returns plus copies of your bank statements. The lending institution may contact them via mail, email or phone to verify your income. This applies to both a mortgage for the initial purchase and a refinancing loan.
So, what does one do if you happen to be self-employed? What if you own your own business?
You can apply for a no income verification mortgage although this cuts into your interest rate shopping. That does not mean you can have no income. It is handy though in several valid situations.
Who Can Use a No Income Verification Mortgage?
While many individuals may find this handy, a few common scenarios exist. You might want to read on if any of these situations apply to you.
- You invest in real estate and carry over passive losses. These eradicate your earnings on paper although you have proven cash flow.
- You work on commission and your income varies vastly from month to month.
- You own your own business and pay yourself, but without a formal paycheck or you are a sole proprietor.
No Income Verification Mortgage Qualifications
Very simply, you qualify for a no income verification mortgage. It requires you to still provide documentation of your income, but a different set of documents than a standard mortgage. You need to have an IRS 1099 or be retired, but with a steady income.
Some organizations, like Mortgage Depot, offer a no income check program. To qualify, you must deposit a 25 percent down payment for the total cost of the purchase transaction and obtain 65 percent Loan to Value (LTV) financing for refinancing. Other requirements exist, but that is the monetary minimum. The Depot’s program is available in 46 states. While you must provide a significant outlay to qualify, you will NOT have to provide the following:
- Tax returns,
- W2’s,
- Pay stubs
Through the program, you can qualify for loan amounts of up to $3 million on investment properties of one to four residential units or condos. In NY, you can use the loans for a primary residence. Other property options include multifamily and mixed-use properties of five units or more, as well as automotive service, office, retail, self-storage and warehouse space. There is no limit to how many properties you can own.
The Self-Employed Borrowers Program
You may not qualify for the no income verification mortgage, but you may qualify for its separate Self-employed Borrowers’ program. This is a different program. If you are self-employed and did not meet the occupancy requirements of the Mortgage Depot No Income Verification Mortgage program, you might qualify for the Self-employed Borrowers’ program. This uses bank statements to verify an individual’s business or personal deposits to calculate income and lets your occupancy include your primary residence.
This probably sounds odd since the lender still is verifying that you have income. These alternatives simply let you use a different form of income to prove you can pay back the loan. No institutions of finance will approve a loan without you proving that you can pay it back. These methods though do allow you to have the bank or credit union consider alternate income which can include the following:
- Social Security benefits,
- Pension funds,
- Child support payments,
- Funds from retirement account distributions,
- Unemployment benefits,
- Disability payments,
- Employment offers for a future position that includes the salary and start date,
- Housing/rental income,
- Capital gains from investments,
- Income from a spouse or partner,
- Trust income,
- Savings or cash,
- VA benefits,
- A government annuity
Potential Lender Requirements
Your lending institution may require a few various items before agreeing to extend a loan to you if you do not have a typical income source. These items range from setting up automated payments to a co-signer.
You would need to set up automated payments so your monthly amount due was deducted on the same date each month from your bank account. This ensures you consistently pay in full and on time.
You might need to provide collateral such as a paid in full vehicle or another property. It is usually easier for a person to obtain a secured loan than any other type.
A cosigner is a third-party individual who applies for the loan with you. If you purchased a new car when you were a teenager, you probably already took out a loan once that used a cosigner. If you fail to pay your loan payments on time, the bank will contact your cosigner for the funds.
Your Credit Is Very Important When Getting a No Income Check Mortgage
Your credit history and credit score still matter. Besides your raw score, any bank will consider your debt repayment consistency and your credit utilization. So, what if you do have less than perfect credit? That is when you have to take a few months – at least six – to improve your score first. Improving your credit is one of the most important mortgage tips to follow.
While you have many ways to check your credit, going to Creditry lets you check your credit, then monitor it, too. You can learn to better manage your credit by using its blog. You can learn important things like:
- How to organize your payment due dates,
- How to request to move a due date,
- Calculating your credit-to-debt ratio,
- The impact of opening or closing a credit line on your credit score
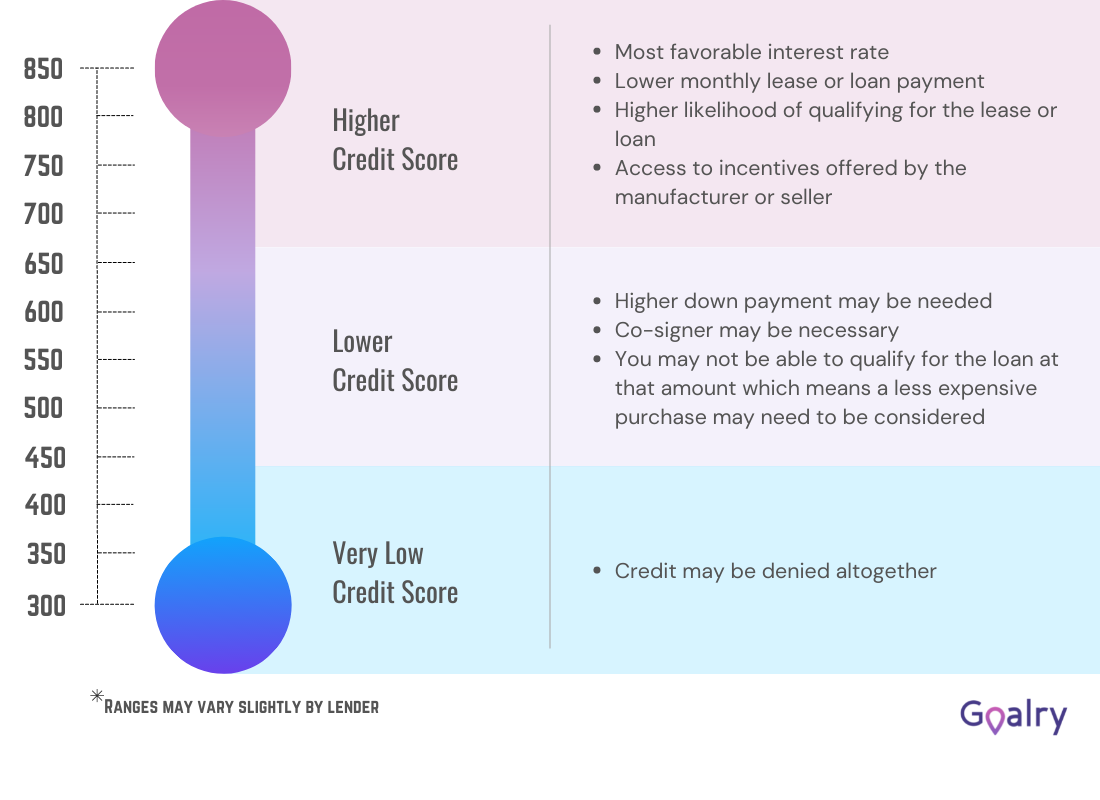
You need to learn those things so you can better manage your credit and build a strong financial history. You also need to check your credit so you know your FICO score. If it is above 679, you need not worry. Credit scores range from 350 to 850 (or 900, depending on the credit bureau). A 680 places you in the good range. If you have a score that places you in the good, very good or exceptional range, you should have an easy time obtaining a loan although you have retirement, variable or unearned income as the source or sources for your monthly payments.
Improve Your Credit Score Fast
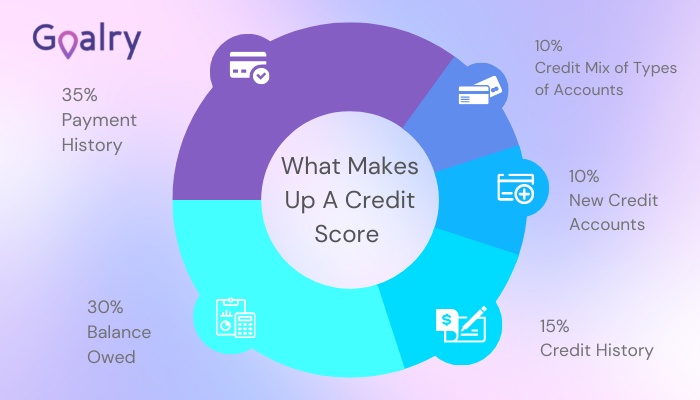
You can also very quickly boost your credit score by altering your credit utilization. When you try to obtain a no income verification mortgage, you will find your credit score means even more. This is the toughest type of mortgage to get. If you can quickly pay off some of your existing debt, you can up your score quickly. Your credit utilization score refers to the total amount of credit you have available versus how much you are using. This comprises 30 percent of your credit score. If you pay down your balances but keep the accounts open, then you can quickly increase your score.
No Income Verification Mortgages Rarer Now
Today it is even harder to qualify for because of the rarity of these loans. This type of mortgage became wildly popular in the early 2000s. While they did help the tiny percentage of individuals with high incomes that could be tough to document, lenders started misusing them for their gain. They began extending the loans to subprime borrowers around the time the housing bubble developed. That made for twice the problem for the financial industry.
It got worse. As lenders continued to extend loans to subprime borrowers, without reliable income, the problem grew. Then those who outright did not qualify began to apply. They knew they did meet the qualifications and they lied on their loan applications to get approved. No income verification mortgages began to get the name “liar loans”. The name liar loans became most applicable in expensive markets where mortgage approvals were extremely rare for all but prime borrowers. The subprime borrowers could not afford the homes for which they applied for mortgages and they defaulted on the loans.
About 2005, the finance industry revamped its low- and no-income verification loans, deciding to try to save themselves by offering more loans. They loosened the requirements which at least meant people no longer had to lie on the applications, but the subprime lenders dropped the qualifications too low in exchange for a higher interest rate. During the period from 2000 to 2007, no income verification mortgage loans more than quadrupled. In those seven years, the loans rose from two percent of home loans to nine percent.
Here’s the deal. Banks and those employed by them have incentives to make loans. Those incentives tipped the scales to them offering too many to people who should not have them. The main reasons are:
- Loan officers earn a commission on every loan. It does not matter if the homebuyer defaults on the loan or not. The loan officer still gets paid.
- Mortgage lenders planned to re-package the loans and sell them to investors as mortgage-backed securities.
- The bank itself makes money on the loan origination fees, so the volume of loans makes them money automatically. Bad or good loan, as long as it went through the system, the bank got paid.
All of the mistakes accumulated and in 2008, the boom went bust, and the banking/financial crisis occurred. According to The Financial Crisis Inquiry Report, by the time the crisis came to a head, investors held more than $2 trillion of the repackaged mortgage-backed securities. They also had invested in about $700 billion of collateralized debt obligations which included mortgage-backed securities.
Delinquencies and defaults occurred the most in what real estate calls sand states – the states of Arizona, California, Florida, and Nevada. Real estate’s expense in these desirable locations caused serious delinquencies – those where payments are late by more than 90 days. That accounted for 13.6 percent of sand state mortgages. Compare that to 8.7 percent nationally.
The Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act of 2010 created a rule set that lenders must meet to end the bad decision-making. It included an “Ability-to-Repay” rule that requires the mortgage lending institutions to confirm each borrower can repay the loan before offering it.
The history lesson comes so you understand just how tough it will be to qualify for one of these mortgages, especially if you live in a sand state. The only loans to which the Dodd-Frank did not apply were those for loan modifications timeshares, reverse mortgages, and temporary bridge loans.
No Income Verification Mortgages Today
A select number of financial lending institutions still offer no income verification mortgages but now the government mandates the qualifications for obtaining one of these loans. The required credit scores range significantly higher and these types of loans come at great expense to the consumer. You will need a score of “very good” or “excellent” to qualify now. This type of mortgage still comes with a higher interest rate than a typical mortgage. The updated law does not apply to business and commercial mortgage purchases.
Final Thoughts
You could purchase a home as a business investment to qualify for a no income verification mortgage. You also could apply for a generic type of personal loan. Loanry provides various educational tools to determine which loan type works best for you. You can complete a small form to get started and it will suggest for you the best loan solution(s). You may get an email of suggestions or you may get automatically forwarded to a lender that offers loans to individuals with your credit history.

Carlie Lawson writes about business and finance, specializing in entertainment, cryptocurrency and FOREX coverage. She wrote weekly entertainment business and finance articles for JollyJo.tv, Keysian and Movitly for a combined seven years. A former newspaper journalist, she now owns Powell Lawson Creatives, a PR firm, and Powell Lawson Consulting, a business continuity and hazards planning consultancy. She earned BAs in Journalism and Film & Video Studies from the University of Oklahoma. She also earned her Master of Regional & City Planning at OU. Her passion lies in helping people make money while reducing risk.