You’re probably familiar with several types of collateral loans without being aware that’s what they’re called. If you’ve ever paid for a home over time or financed an automobile, you’ve probably used a collateral loan. In a typical mortgage, the home itself acts as security for the loan; if you don’t make your house payments, the lender may take it from you. A car or truck loan – especially on a new vehicle – is quite similar; if you miss enough payments, the dealer, bank, or credit union can take (or take back) the automobile in question.
Collateral Loans: What Are They and How They Work
At their most basic, collateral loans are any loans backed up by collateral – the stuff of value which lenders can take ownership of if the borrower is unwilling or unable to fully repay the loan in a timely manner.
If that sounds somehow harsh or unfair, keep in mind that without collateral loans, most of us would never be able to afford those sorts of big ticket items. Our home buying options, for example, would be to save up until we had enough to pay cash, or live with our parents until they passed on and left us their house. Personally, I don’t find either of those particularly promising.
Thanks to the modern mortgage structure, however, almost anyone can finance their home over a 15 or 30-year period. Lenders still care about your credit history and such, but they have the home itself as collateral as well, which allows the sorts of ridiculously low interest rates we’re currently experiencing in home loans.
Let’s Talk Terms (The Terminology of Collateral Loans)
Before we push ahead with different situations in which collateral loans might be a good option, it might be helpful to clarify a few of the terms I’m going to use or which you’re likely to encounter if you’re researching collateral loans for your own use.
Collateral / Collateralization
As you’ve no doubt picked up on by now, “collateral” refers to the home, car, or another item of value you offer as security for a loan. When you use your property or assets this way, they become “collateralized.” The term “collateralization” can be used in reference to the process itself or in reference to the loan or the items offered up as security.
You will thus hear that the loan has been “collateralized” or remember that you can’t sell your truck because it’s “collateralized” for a small personal loan on which you’re still paying. You may also come across a reference to the “collateral value” of your property, referring to the amount it’s worth as collateral. This may be different than what you paid for it or how much it’s worth to you personally.
Secured Loans / Security
If your loan is backed up by collateral, it’s a “secured loan.” The term references the lower risk taken by the lender when an item of value is being offered as “security”. If you don’t make your payments, they take ownership of your collateral and sell it to recoup their losses. That’s not really what lenders want to do; they’re not looking to make a living selling used boats or whatever. What this does, however, is enable lenders to offer loans they might not otherwise, based on your credit score or credit history, and to extend better terms than they would even if they did approve the loan minus your collateral.
Unsecured Loans
If your loan is NOT backed up by collateral, it’s an “unsecured loan.” These rely entirely on your creditworthiness as indicated by your credit history and current credit score. Lenders may, to a lesser extent, factor in your current reliable income and job situation.
Failure to make your payments on time, or to make them at all, will hurt your credit (making it even harder to borrow money on decent terms in the future) and may lead to collections or legal action, but it WON’T directly result in losing your home or car because those things haven’t been offered up as collateral. Because this means greater risk to the lender, expect lower loan limits and higher interest rates on most unsecured loans.
Assets
Your “assets” are anything you own that has financial value and are thus might be used as collateral. Some assets, like your home or car (assuming you have enough “equity” in them – that you’ve paid enough on THEIR loans that you “own” part of their value) are fairly typical as collateral. They’re easily converted into cash if necessary and have a fairly predictable value.
Savings accounts or investments are also “assets”. Their value to lenders depends on how “liquid” they are (how easily they can be transferred and converted into cash) and the likelihood they’ll hold their value over the life of your “secured” loan.
Atypical assets – your semi-rare comic book collection, those sacred mummy heads you inherited and are currently on loan to the local museum, that one-of-a-kind triple-neck 8-string guitar designed, built, and signed by Rick Nielsen of Cheap Trick – may be more difficult to use as collateral since their value is slightly more subjective and they’d be more difficult to convert to cash.
Equity
This is the “stored value” you own in various forms. If you’re halfway through paying off your car, and its current value is $12,000, you have around $6,000 worth equity in it. The same holds true for your home. If its market value is currently $195,000 and you owe $115,000, you have equity of about $80,000 to work with (although most lenders won’t advance more than 80% of the value of whatever you’re collateralizing). Savings accounts or investments are a bit easier to compute. If you have $7,341 dollars in savings, that’s equity worth $7,341.
Note: We’re using “assets” and “equity” more or less interchangeably here, but technically they’re not the same. In the most formal financial sense, “assets” tend to be things of value – tangible items – that have financial value. “Equity,” when having a very serious business-type discussion, refers to the cash value of everything you could convert to cash easily, minus existing liabilities.
In other words, Equity = Assets – Debts/Obligations. This distinction is useful in some contexts, but for our purposes it’s like arguing about whether the U.S. is a “democracy” or a “republic.” It depends on who’s using the terms and what they’re using them for.
Liquidity
You’re no doubt aware that liquids easily change form to adapt to circumstances. Pour your drink into a tall, thin glass, and your drink fills up the tall, thin shape. Spill it on your keyboard, and it quickly fills in every crevice and finds its way into the inner workings of your computer. “Liquid Assets” are those easily converted into cash. “Liquidity” refers to how easy (or not) this conversion is. Used cars in good shape have great liquidity; rare books in ancient languages may be just as valuable, technically, but are harder to immediately turn into cash.
Interest
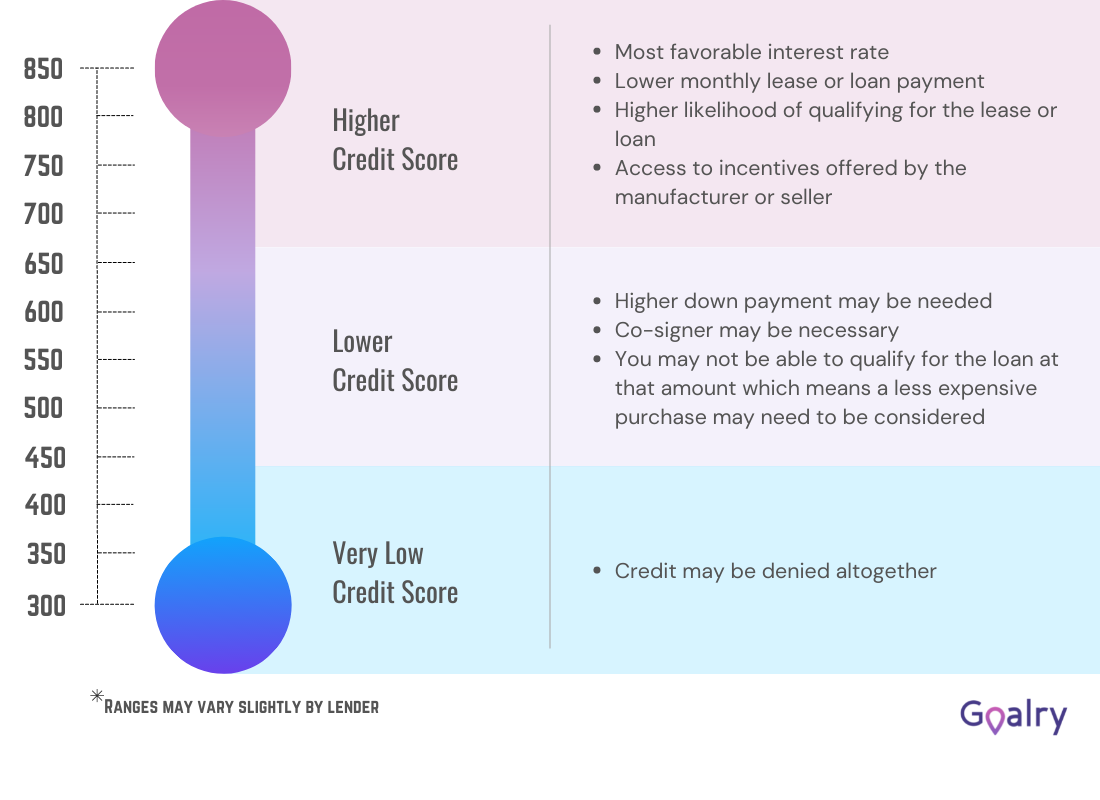
Interest is the primary cost of a loan. Figured as a percentage of the total borrowed. Interest rates tend to be higher if you have a limited credit history or a low credit score. Because the lender is assuming a greater risk by loaning you money and hoping you’ll repay. Greater risk means greater reward, at least in modern American capitalism. Interest rates are typically lower if you have a good credit score because the risk is less. The same is true if you’re able to offer up collateral of greater value than the loan amount. The same rate of interest can be computed in numerous ways (which we won’t go into here). So it’s important to pay attention to the details when rate shopping for your best loan options.
Default / Recourse
“Default” is a fancy word for “stopped paying” and “recourse” is a fancy word for what the lender has a right to do if you stop paying. If you still owe money on a loan and you stop paying for any reason, you’ll eventually be declared “in default”. Whether this is triggered at 30 days, 60 days, or longer, and what penalties are triggered once you’ve “defaulted” varies from loan to loan. This is the point, however, at which lenders can report you to a collection agency, take legal action, or seize control of whatever assets you collateralized to secure the loan.
So, to summarize, the reason you may be asked to offer part of your assets as collateral is so that the lender has recourse if you default. You agree because you wanted to secure a lower interest rate than you could get with an unsecured loan. And you know you have sufficient equity for adequate collateralization. (See how much fancier that sounds than “I had to sign a paper saying the bank will take my truck if I don’t make my loan payments”?)
Advantages of Collateral Loans
There are a wide variety of collateral loans, each with its own features and potential pitfalls.
In general, however, there are a number of positives to collateralizing your assets in order to get the best terms on a secured loan. (I thought we might get more comfortable with all the fancy terms if we used them more.) What I’m saying is, there are reasons you might want to explore collateral loans for whatever your current needs might be.
Available for Poor Credit
If you have limited or poor credit, offering collateral might make the difference between getting a loan and being denied. Lenders have to make a reasonable profit – that’s how business works. In their case, that means two primary things have to happen with some regularity. First, they have to loan out money at interest (with interest being their profit), and second, they have to get repaid with a minimum of extra effort. If it costs them twice what they’re making in interest to track you down and force you to pay, the lender loses money in addition to your credit being damaged. That’s no fun for anyone. With collateral, there’s a better chance you’ll pay, and better protection for the lender if you don’t.
Lower Interest Rate
Offering collateral can secure you a better interest rate. This works for the same reasons we just discussed a loan approval. Lower risk means lenders can offer better terms – especially a lower interest rate. They don’t have to make a LOT on each loan if they’re relatively sure of repayment. Plus, lenders want you to be happy and say nice things about them. And come back to them for your future financial needs as well. Reputable lenders aren’t looking to “defeat” you; they want you both to come out OK on the other end because that’s what’s best for business.
Your Collateral Allows You to Take a Higher Amount
You may be able to borrow a larger amount if you have sufficient collateral. Let’s say you’re planning some major home renovation and remodeling. You’ve run the numbers, and it’s the best thing for your family now and the value of your home in the coming years. But the estimates you’ve gathered for getting the work done are higher than you’d hoped, and your credit is OK, but not great. Being able to use your home’s equity as collateral gives lenders the security they need to extend you the full amount. The risk is less for them but greater for you… if for some reason you’re unable to make your payments in the future, you could lose your nicely remodeled and renovated home.

Collateral Loans Provide “liquidity”
If your wealth is largely tied up on assets with low liquidity, it might make more sense to borrow against them than to convert them in order to finance whatever you need to do. This is more often the case with businesses than with personal collateral loans.
Collateral Loans are a Great Way to Build Credit
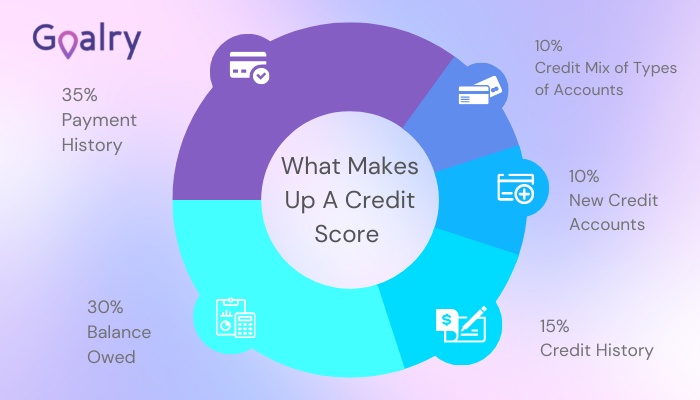
One of the realities of modern American life is that almost all of us need access to financing multiple times over the years. At some point, you’re going to want to buy a home, finance a car or truck, pay for a wedding, take a vacation, pay off medical bills, or start a small business. Each time you do, potential lenders will check your credit. The higher it is, the more flexibility you’ll have and the better the terms you’re likely to be offered. The lower it is, the more difficult it is to do, well… pretty much everything.
Collateral loans are also a good way to finance debt consolidation. If you’re ready to get serious about your household budget and take more effective control of your personal finances, collateral loans can act as a foundation for making that happen.
You are not your credit score. It’s not a reflection on you as a person. It is seriously inconvenient, however, and expensive over time. A few small collateral loans allow you to obtain credit. But just as importantly, as you pay them back, you’re building your credit history and raising your credit score. So that’s pretty awesome.
Potential Pitfalls of Collateral Loans
Well, there’s the biggie – if for any reason you’re unable to repay the loan in full, you can lose whatever you’ve put up as collateral. Even if the lender takes your collateral and sells it to recoup their investment, late or unpaid loans will still damage your credit substantially. As with ANY loan in ANY form for ANY reason, make sure you have a budget. And a good reason to borrow and a clear pathway to repayment before you even begin rate shopping.
There are a few minor inconveniences as well. Obviously you have to have an asset or assets of value in order to offer them up as security. There’s more paperwork than with an unsecured loan. Because lenders will require a formal valuation of the assets you’re offering as collateral. That means it may take a bit longer to get your loan as well.
Final Thoughts
We’re never going to tell you what the best choice for you or your family is when it’s time to borrow or refinance. What we will do is try to give you all of the information necessary for you to make an informed decision.
It probably won’t surprise you to know that we’re big fans of online lending around here. We don’t loan money ourselves, but we maintain a curated database of reputable online lenders who specialize in creative solutions and surprisingly competitive terms. And many of them, as it turns out, aren’t as quick to request collateral as traditional financial institutions. I’m not saying it never happens – just that you’d be surprised at the options you might have.
If you’re looking to borrow or refinance, consider all of your options before making your final decision. Collateral loans are ONE of those options, but they’re probably not the ONLY one.
Let us know if we can help.

Blaine Koehn is a former small business manager, long-time educator, and seasoned consultant. He’s worked in both the public and private sectors while riding the ups-and-downs of self-employment and independent contracting for nearly two decades. His self-published resources have been utilized by thousands of educators as he’s shared his experiences and ideas in workshops across the Midwest. Blaine writes about money management and decision-making for those new to the world of finance or anyone simply sorting through their fiscal options in complicated times.